Blogs, Products
How Do Robotic Arms Work?
Robotic arms are masters of manipulation, and their prowess lies in the intricate principles governing their operation. These principles play…
35 minute read
In This Article
The realm of robotics undergoes continuous evolution, marked by machines growing increasingly versatile and adaptable. At the core of this transformation lies the essential component enabling robots to engage with the physical world – end-of-arm tooling (EOAT), which plays a pivotal role in defining a robotic arm’s utility across various industries.
How an EOAT interacts with its surroundings is the determining factor in its seamless integration into diverse workflows.
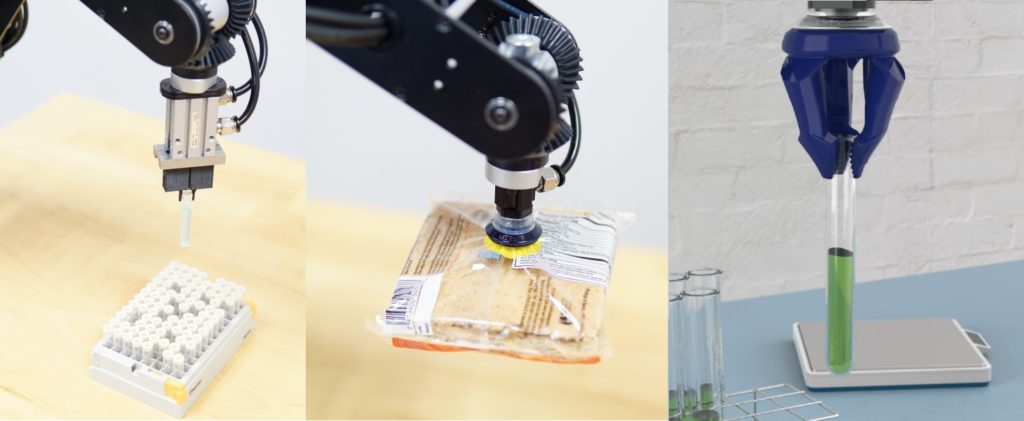
The gripper is one such end-of-arm tool that makes a robotic arm versatile and efficient for different processes like pick and place, labeling, camera handling, and vial handling, to name a few.
Whether you’re a robotics enthusiast or a tech-savvy professional, this guide is your gateway to understanding the essential components that enable robots to interact with the world around them.
A gripper is a mechanical or robotic device designed to grasp, hold, manipulate, or transport objects. It serves as the “hand” or end-effector of a robotic arm or automation system, allowing the robot to interact with the physical world by gripping and releasing objects.
Various types of robot grippers are revolutionizing automation across industries.

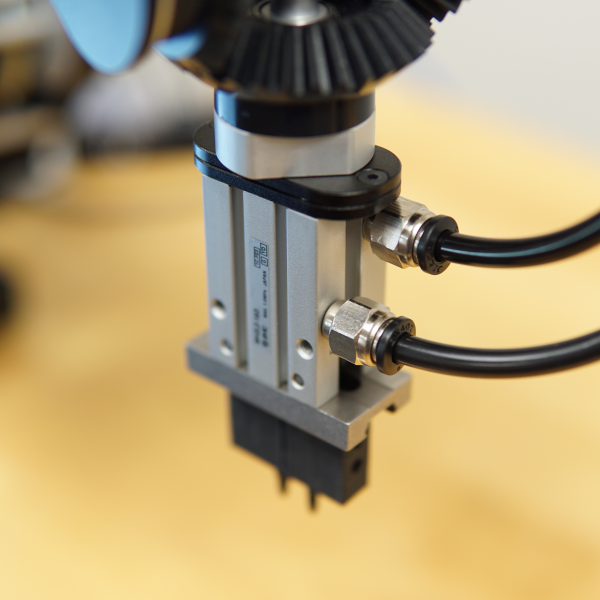
Parallel jaw grippers stand out as one of the most prevalent and versatile gripper types employed in robotics. Comprising two opposing jaws capable of moving parallel to each other, they boast a design that lends itself effectively to grasping objects of diverse shapes and sizes. Be it the delicate handling of small electronic components or the secure grip of larger, irregularly shaped items, parallel jaw grippers excel in executing precise pick and place operations.
Parallel jaw grippers often feature a range of jaw designs and materials tailored to suit diverse applications.
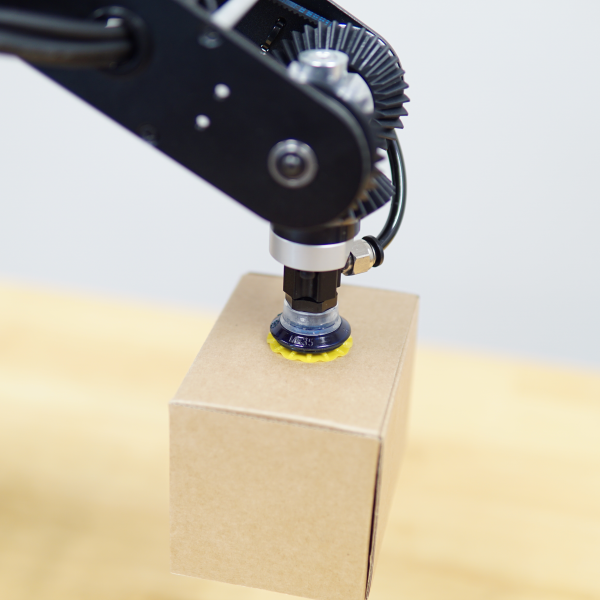
Also known as Suction grippers, these are particularly effective at handling flat and smooth-surfaced items such as glass, plastic, and metal sheets. A Vacuum gripper comprises a vacuum pump that creates suction through a network of channels or holes in the gripper’s pad.
Dorna, known for its advanced robotic arms, also offers a range of vacuum grippers designed to complement its robotic solutions, providing even more versatility and efficiency in various automation applications.
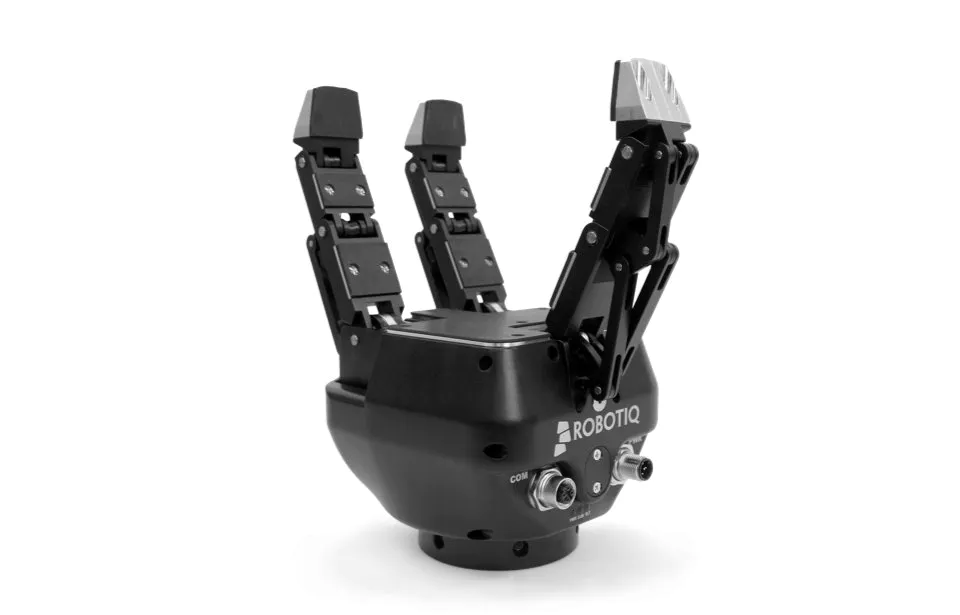

When it comes to manipulating objects with irregular shapes or intricate geometries, finger grippers offer the perfect solution. These grippers are equipped with multiple fingers or digits that can conform to the object’s shape during grasping. These fingers can be crafted from rigid materials for stability or soft, compliant materials to safeguard delicate items, depending on the specific application.
Pneumatic grippers utilize compressed air to control the movement of their jaws. They are known for their speed and ability to provide a strong grip, which makes them a preferred choice for high-speed applications on assembly lines. These grippers are often found in industries like automotive manufacturing and electronics assembly.
A recognized cutting-edge robotic arms provider, Dorna’s automation solutions portfolio extends to a range of pneumatic grippers, expanding Dorna’s capability to address a broader spectrum of industrial needs.


Electromagnetic grippers leverage magnetic fields to hold and manipulate ferrous (magnetic) objects, such as metal components. These grippers are highly effective when a strong and stable grip on metal objects is required.
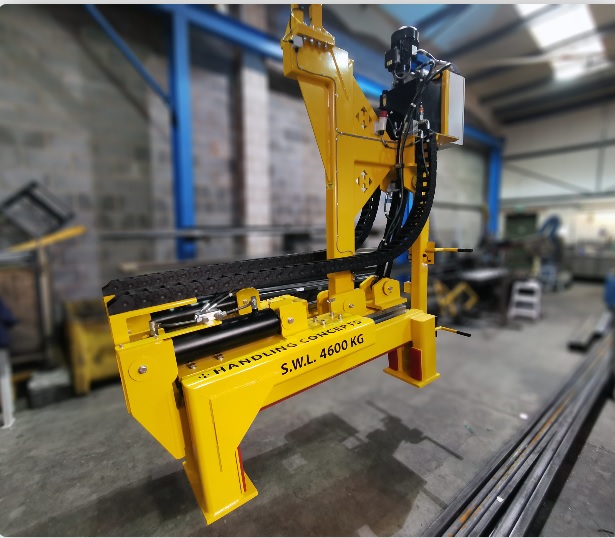

These grippers are the heavyweights of the gripper world. They employ hydraulic fluid to precisely operate their jaws, particularly excelling in tasks that entail handling sizable and weighty objects demanding substantial gripping force.
These grippers frequently boast robust construction and secure sealing mechanisms to eliminate hydraulic fluid leakage. They offer versatility through various jaw configurations, encompassing parallel jaws, angular jaws, and even customized designs, all tailored to meet the precise demands of specific applications.
Grippers are the unsung heroes of robotic arm automation that enable these machines to perform a wide range of tasks with precision and efficiency. Whether it’s the adaptability of finger grippers, the strength of hydraulic grippers, or the precision of vacuum grippers, each type has its unique set of advantages and applications.
Dorna, a leading provider of innovative robotic solutions, offers a wide variety of versatile and efficient grippers. Explore how our grippers can enhance your industrial operations.
As automation continues to reshape industries, the selection of the appropriate gripper becomes increasingly vital for optimizing efficiency and productivity. By gaining insights into the various types of robot grippers and their capabilities, businesses can make sure that their choice aligns with their needs.
Determine how applicability of the Dorna’s grippers caters to your specific needs.
Blogs, Products
Robotic arms are masters of manipulation, and their prowess lies in the intricate principles governing their operation. These principles play…
35 minute read
Blogs
Robotics and automation may be related concepts, but they have significant differences. In essence, robotics is a subset of automation…
25 minute read
Blogs
Automating material handling tasks like Pick-n-place or Material cutting can improve efficiency, precision and cost-effectiveness.
12 minute read
Blogs
End-of-arm tooling (EOAT) is a cornerstone of the automation revolution. It serves as the vital link between robots and their…
34 minute read